Search Results
Results for: 'The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H . • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■ In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■ HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • HC1 in gastric juice is important for the digestion of proteins. • HCl kills bacteria in food by destroying their proteins. Weak acids - role in the body ■ Carbonic acid is produced from CO2 and H2O. ■ H2CO3'
The pH scale - Strong acids and Weak acids
By: HWC, Views: 6715
The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H+. • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■ In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■ HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • H...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 6359
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
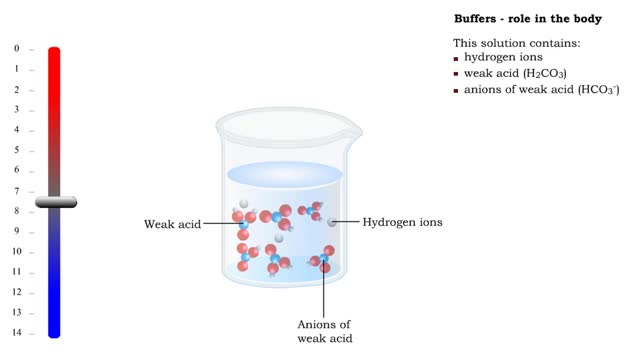
Buffers definition and the role of buffer in the body
By: HWC, Views: 6804
■ Too many H+ break hydrogen bonds and a protein comes apart. ■ Buffers react with excess H+ to protect proteins from breaking down. ■ Buffers consist of weak acid plus anions of that weak acid. This solution contains: • hydrogen ions • weak acid (H2CO3) • anions of we...
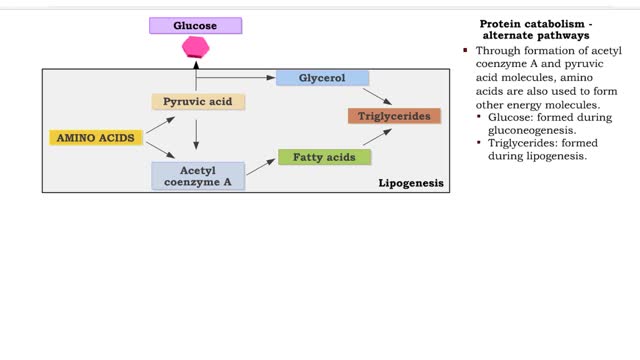
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 7032
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
By: HWC, Views: 6592
Acids and bases are found all around your house. For example, if you open your pantry or refrigerator, you might see a lot of acids. Fruit juice, soda pop, vinegar, and milk are all examples of acids. The word acid actually comes from a Latin term meaning ''sour.'' Many materials, like sugar for ...
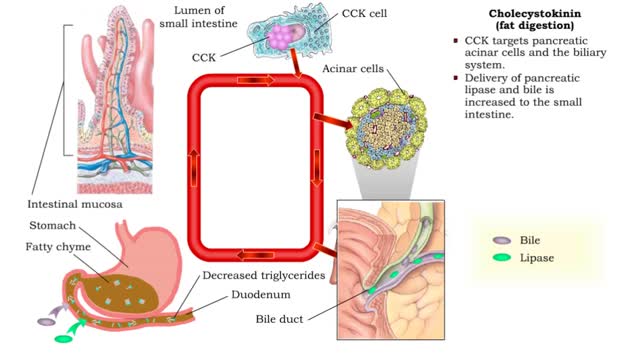
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 6395
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
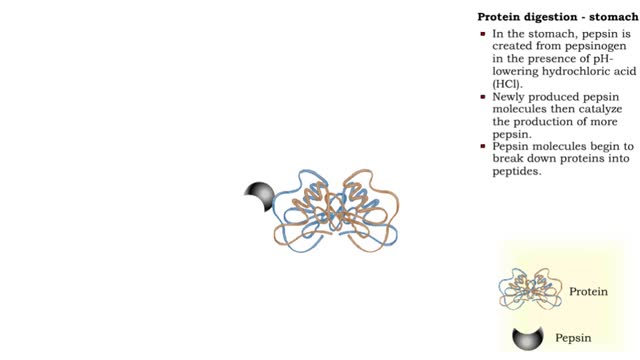
Protein digestion - stomach & small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 6084
• Protein digestion occurs in the stomach and small intestine. • The stomach enzyme pepsin initiates the process. • Pancreatic and intestinal brush border enzymes complete the digestive process. • In the stomach, pepsin is created from pepsinogen in the presence of pH-lowering hyd...
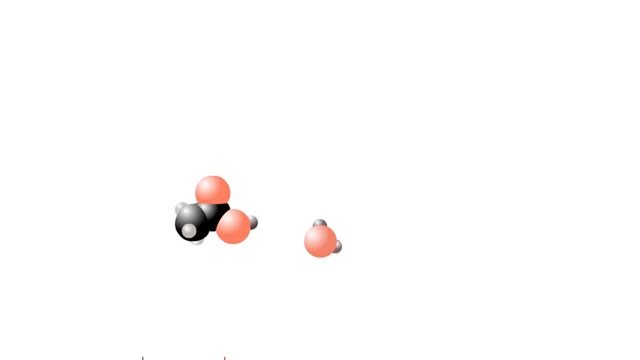
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 5485
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
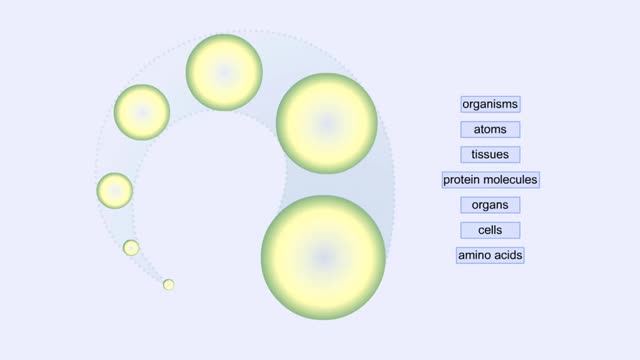
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 6149
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
Advertisement